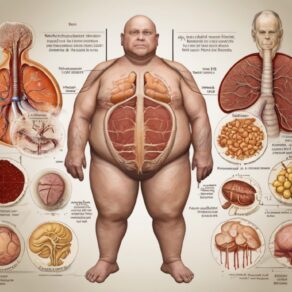
Metabolic dysfunction is a term that encapsulates a range of disruptions in the intricate web of biochemical processes that govern energy production, utilization, and storage within the human body. This article aims to provide a clear and comprehensive definition of metabolic dysfunction, exploring its key components and implications for overall health.
I. Defining Metabolic Dysfunction: A. Overview of Metabolism:
- The fundamental role of metabolism in the body
- Conversion of nutrients into energy through metabolic pathways
- Balance between anabolism and catabolism for optimal function
B. Metabolic Homeostasis:
- The importance of maintaining equilibrium
- Hormonal regulation and enzymatic control
- Cellular and systemic implications of metabolic stability
II. Components of Metabolic Dysfunction: A. Genetic Factors:
- Inherited metabolic disorders and their impact
- Genetic predispositions to metabolic imbalances
- How genetic variations can disrupt enzymatic functions
B. Lifestyle Influences:
- Sedentary behavior and its contribution to metabolic dysfunction
- Dietary choices and the role of nutrition in metabolism
- The impact of sleep patterns and stress on metabolic health
C. Hormonal Imbalances:
- Insulin resistance as a common hormonal disruption
- Dysregulation of thyroid hormones and metabolic rate
- Cortisol and its role in stress-induced metabolic dysfunction
III. Manifestations of Metabolic Dysfunction: A. Obesity and Metabolic Syndrome:
- Link between excess adiposity and metabolic disruption
- Diagnostic criteria for metabolic syndrome
- Cardiovascular implications and other associated risks
B. Type 2 Diabetes:
- Insulin resistance leading to dysregulated blood glucose levels
- Long-term complications and organ damage
- The relationship between obesity and type 2 diabetes
C. Dyslipidemia and Cardiovascular Complications:
- Altered lipid profile and its impact on cardiovascular health
- Atherosclerosis and metabolic dysfunction
- Managing dyslipidemia for improved metabolic outcomes
IV. Diagnosis and Assessment: A. Biomarkers and Blood Tests:
- Identifying key markers of metabolic dysfunction
- Blood glucose, insulin, and lipid profiles
- Assessing inflammatory markers and their significance
B. Imaging Techniques:
- Role of medical imaging in assessing metabolic health
- Visualizing adipose tissue distribution and organ function
- Non-invasive methods for metabolic assessment
V. Implications for Overall Health: A. Systemic Effects:
- Impact on various organs and body systems
- Association with chronic conditions and diseases
- The role of inflammation in systemic consequences
B. Psychosocial Dimensions:
- Influence on mental health and well-being
- The interconnectedness of metabolic health and psychological factors
- Addressing the holistic aspects of metabolic dysfunction
VI. Addressing Metabolic Dysfunction: A. Lifestyle Interventions:
- Importance of diet and physical activity
- Behavioral changes for improved metabolic health
- Developing sustainable habits for long-term well-being
B. Medical Interventions:
- Pharmacological approaches to manage metabolic dysfunction
- Insulin-sensitizing agents and antihyperglycemic medications
- Advancements in medical therapies and emerging treatments
Conclusion: Metabolic dysfunction represents a dynamic and multifaceted challenge to human health, encompassing genetic, lifestyle, and hormonal influences. By understanding its definition and components, individuals can become proactive in adopting preventive measures and seeking appropriate interventions. This comprehensive exploration aims to empower readers with insights into the intricacies of metabolic dysfunction, fostering a proactive approach to achieve and maintain metabolic health.